Tematica’s Take on Mnuchin’s Reforms and Growth Prospects
There are several drivers of a company’s business as well as the price of its shares, assuming it is publicly traded. We described many of these in Cocktail Investing: Distilling Everyday Noise into Clear Investment Signals for Better Returns, but a short list includes new technology, regulatory mandates, the overall speed of the global economy and new policies flowing out of Washington. From a business perspective, more regulations and taxes tend to drive costs higher, leaving companies with smaller profits to spread across developing new products and services, implementing new technologies and creating more jobs – in other words investing for the company’s future.
We’re seeing this today in the restaurant industry, which is struggling with the impact of higher minimum wages as companies like McDonald’s (MCD) and others look to bring mobile ordering, as well as in-store kiosks like those found at Panera Bread (PNRA), to market. There has been much made about the low to no growth in the US economy over the last several years, but headwinds, like our aging population that has people shifting from spenders to savers and rising consumer debt levels that weigh on disposable income levels and consumer spending, make prospect for growth challenging.
Last week Treasury Secretary Steve Mnuchin reiterated in his testimony in front of the Senate Banking, Housing, and Urban Affairs Committee that the Trump administration’s goal of 3 percent or better GDP is achievable provided, “we make historic reforms to both taxes and regulation.” Mnuchin went on to say, “he’s got 100 bodies working on tax system reform and that they’re working on far more than just undoing the Dodd-Frank Act” including overhauling housing finance reform.
Over the weekend in a radio interview, Mnuchin noted, “The good news is that [the administration and Congress] all agree on the fundamental principles: simplifying personal taxes, creating a middle-income tax cut and making our business taxes more competitive.” Mnuchin went on to acknowledge that over the past eight years, the US economy has had very low growth, but “tax and regulatory changes and better trade deals” can unleash more historically typically growth rates in this country,” with “sustainable levels of 3 percent growth.”
The key word employed by Mnuchin is “reform,” and no matter which definition of the word offered by Merriam Webster – “to amend or improve by change of form or removal of faults or abuses” or “to put an end to (an evil) by enforcing or introducing a better method or course of action” – it’s rather clear Mnuchin’s language suggests something far more historic than a temporary tax cut or other one-time band aids like we’ve seen in recent years. That resetting should help reduce regulatory and litigation costs, but also a lower corporate tax rate, which would benefit predominantly US based companies like Verizon Communications (VZ), CVS Health (CVS), Walt Disney (DIS), Norfolk Southern (NSC) and others as well as their shareholders.
With true regulatory and tax reform, there would be the added benefit of certainty or at least greater certainty that would allow for longer-term corporate planning. It’s rather well understood the stock market abhors uncertainty, but uncertainty in the form of short-term tax cuts and ones that are about to expire as well as a shifting regulatory environment wreak havoc on corporate planning and subsequently spending. One example is Research & Experimentation Tax Credit (better known as R&D Tax Credit) was originally introduced in the Economic Recovery Tax Act of 1981 with an original expiration date of December 31, 1985.
Flash forward a few years, and the credit has expired eight times and has been extended fifteen times with the last extension expired on December 31, 2014. Not exactly a boon to corporate planning, but in 2015, Congress made permanent the research and development tax credit, which now allows more consistent planning and product development at companies ranging from Apple (AAPL) and Facebook (FB) to II-VI (IIVI) and Oracle (ORCL), not to mention food and beverage companies like Coca-Cola (KO) and PepsiCo (PEP). Douglas L. Peterson, President and Chief Executive Officer of S&P Global Inc. summed it up well when he said, “If we knew where the cost was going…and we’re able to predict it over the long run, we could have a completely different planning cycle and invest in the long run.”
While these reforms are likely to help reignite growth in the US economy, the stark reality is between increased spending to rebuild US infrastructure as well as the US military and ensuring entitlement programs are in place for our aging population, there is a deficit funding gap at least in the short to medium term that will need to be addressed. While there are several mechanisms being bandied about, a recurring one is the Border Adjustment Tax. There are those that oppose it, particularly retailers that source heavily from outside the US, but the argument for the Border Adjustment Tax is that it would help level the playing field between imported goods and those crafted within the US as well as encourage companies to source within the US, thereby developing industries and creating jobs.
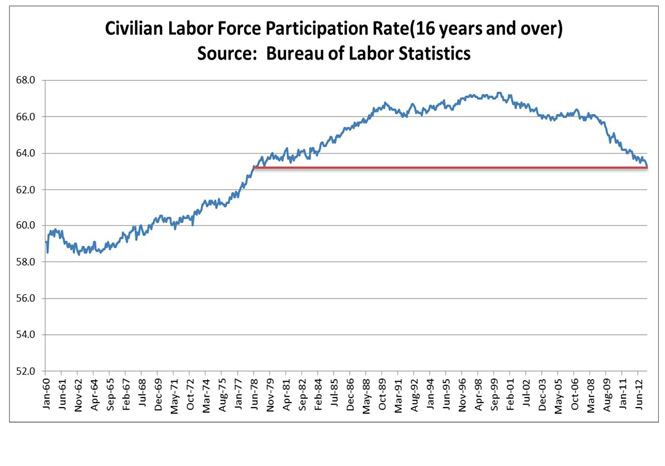
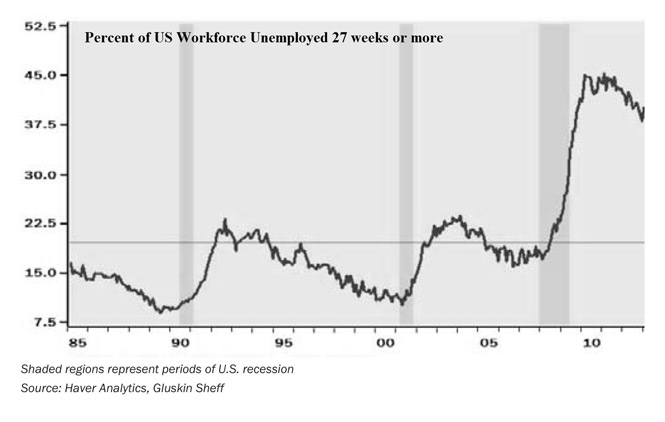
The challenge here is that with the gap between Job Openings and Hirings already well above historical norms as companies struggle to find the right talent for open positions as we sit at what has been the lower range of the unemployment rate over the past fifty years, who is going to take these jobs? Regular Tematica readers will quickly recognize how this pertains to our Tooling and Re-tooling investment theme.

We frequently discuss here at Tematica Research how economic growth requires that either the labor pool grows and/or productivity must rise. If companies are able to keep more of their income thanks to tax cuts, they can invest back into their own operations so that the productivity of their workforce improves. That being said, cutting corporate tax rates doesn’t guarantee that companies will do such reinvestment as they could also look to return the additional funds to investors through dividends, fund buyback programs or hold onto it if there is concern that times could get tough in the near to medium-term future. Investors need to assess the overall economic conditions and business drivers as well as other incentives facing companies when it comes to decided just what to do with those tax savings.
As Team Trump and his allies, including Mnuchin, look to reset the administration’s timetable for meaningful reform, investors should begin doing their homework on which companies stand to benefit. If we see lower corporate tax rates like those being discussed, we could see greater earnings falling to corporate bottom lines, which could spur shares in those companies higher, outside of any decision on just what to do with those newly saved funds. If we see infrastructure spending beginning, it offers another shot in the arm for companies like US Concrete (USCR), Granite Construction (GVA) and aggregates companies like Martin Marietta (MLM). Any boost in defense spending would likely bode well for companies such as General Dynamics (GD), Raytheon (RTN) and Northrop Grumman (NOC).
The key is for investors to develop their wish list today and be ready to strike once we know the particulars on the actual reforms. While that is likely a sound strategy, we would suggest investors go one step further and utilize our thematic perspective to identify those companies already benefiting from pronounced multi-year tailwinds that could also benefit from tax and regulatory reform, rather than being dependent solely on these reforms making it through the D.C. sausage factory.