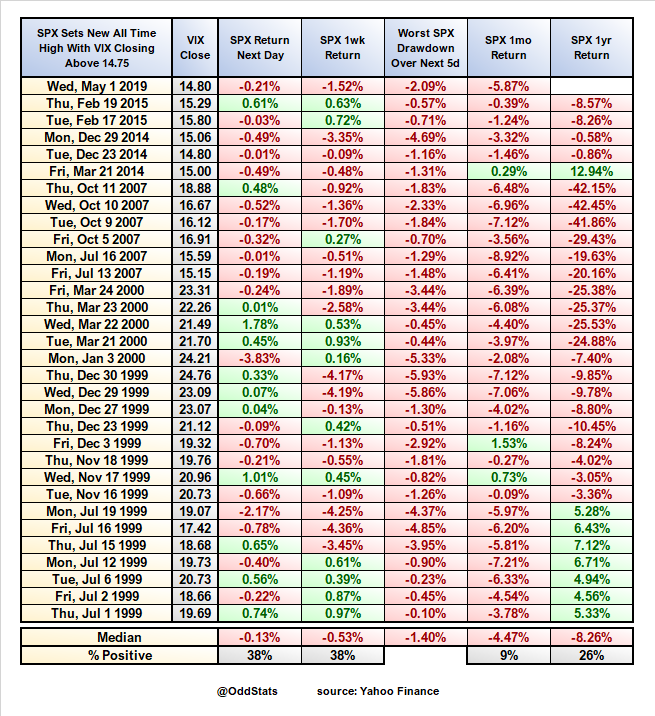
The Magic 8-Ball Market
Last week ended with equity markets taking another dive that accelerated into Friday’s close as the trade war with China intensified heading into its eighteenth month with China announcing that it will impose retaliatory tariffs on US goods. The S&P 500 closed down 2.5% for the third time this month. After the close President Trump launched a twitter storm to announce additional retaliatory tariffs in response to China’s. So that’s going well.
Investors face challenging times as the major market movers have simply been words (tweets) coming from politicians and bureaucrats, the prediction of which is akin to assessing the next missive from a Magic 8-Ball.
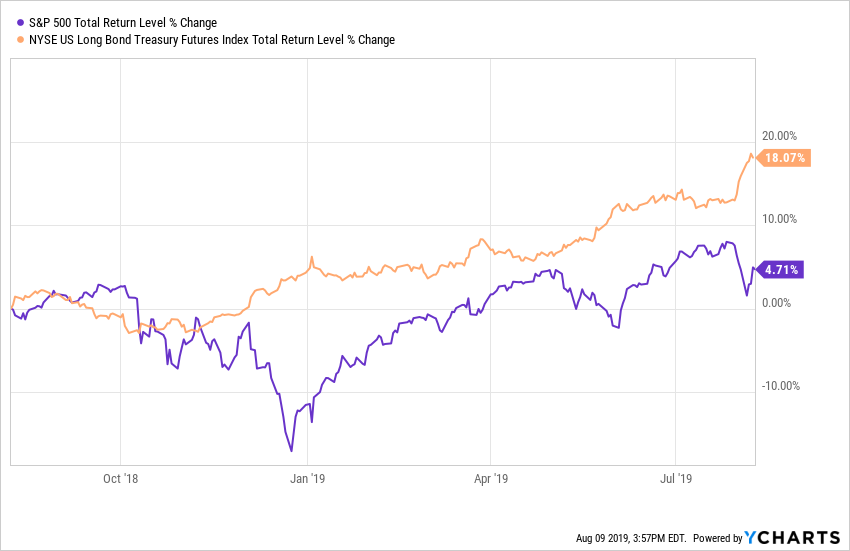
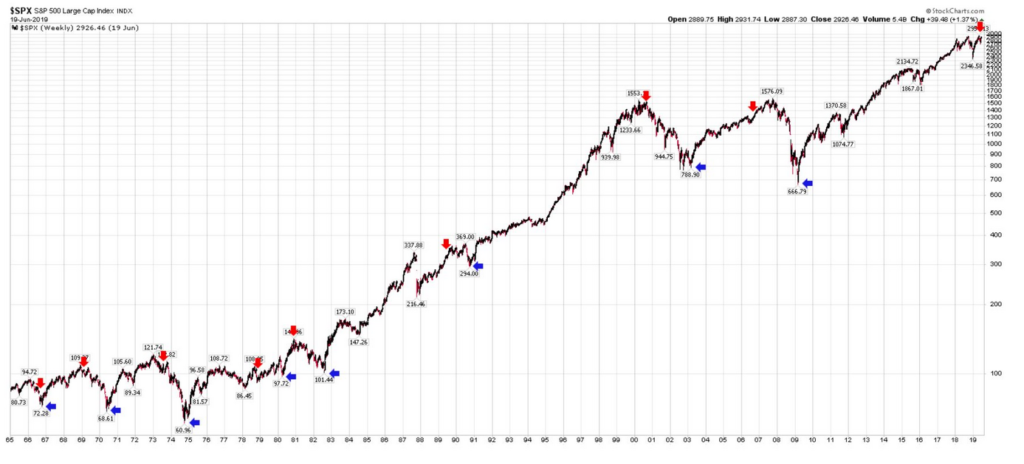
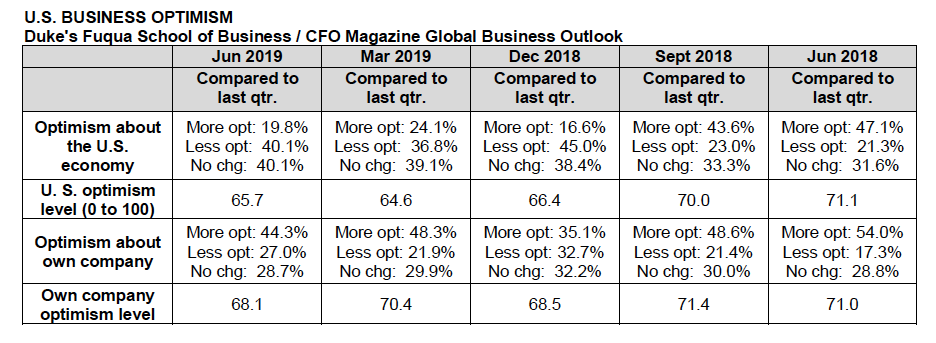
While many continue to talk about the ongoing bull market, the major US equity market indices have seen four consecutive weekly declines and are all in the red over the past year with the small cap Russell 2000 down well over 10%, sitting solidly in correction territory. On the other hand, this year has seen the strongest performance out of long-maturity Treasuries since at least 1987.
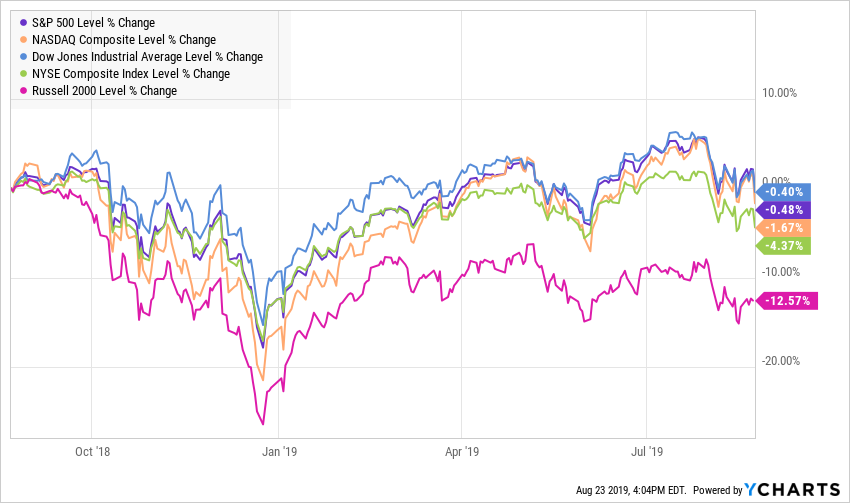
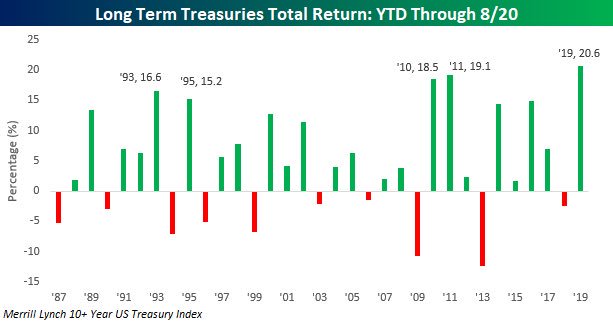
How many bull markets see the total return for the long bond outpace the S&P 500 by over 16%.
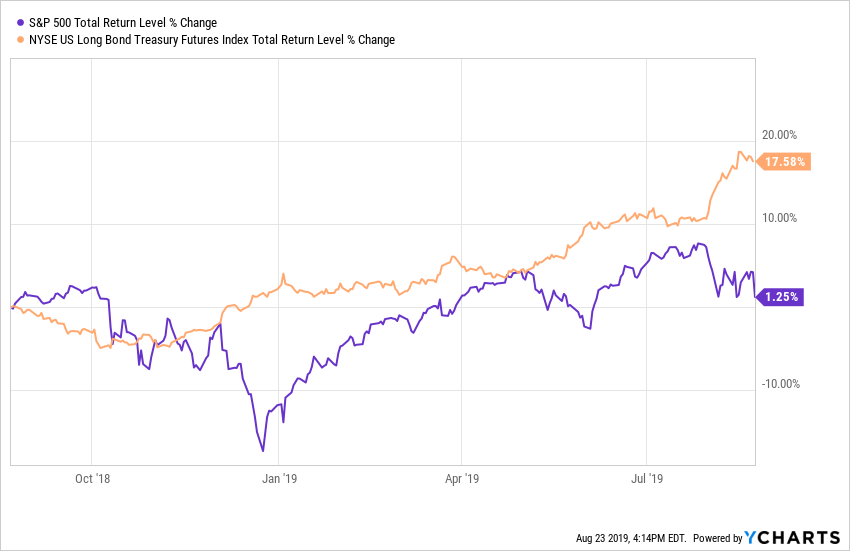
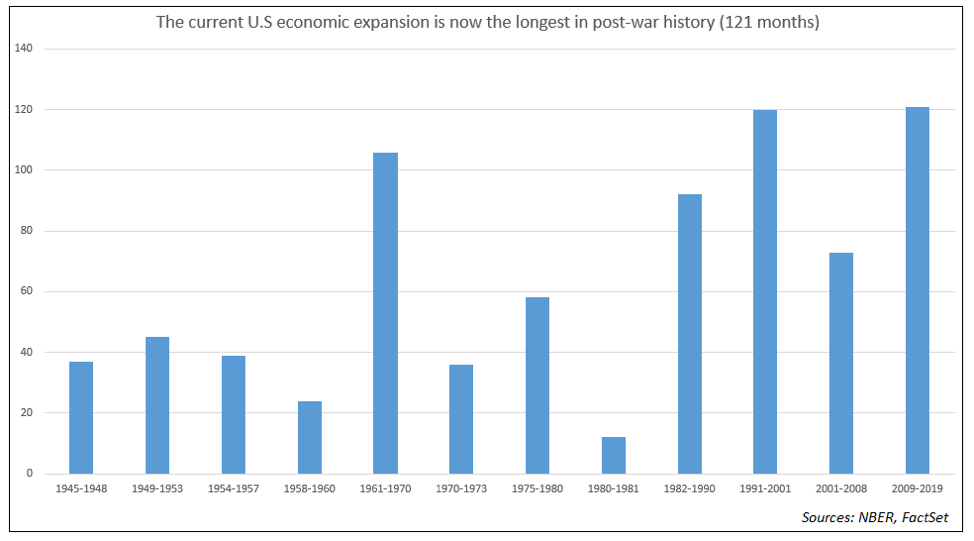
This comes at a time when the domestic economy is in
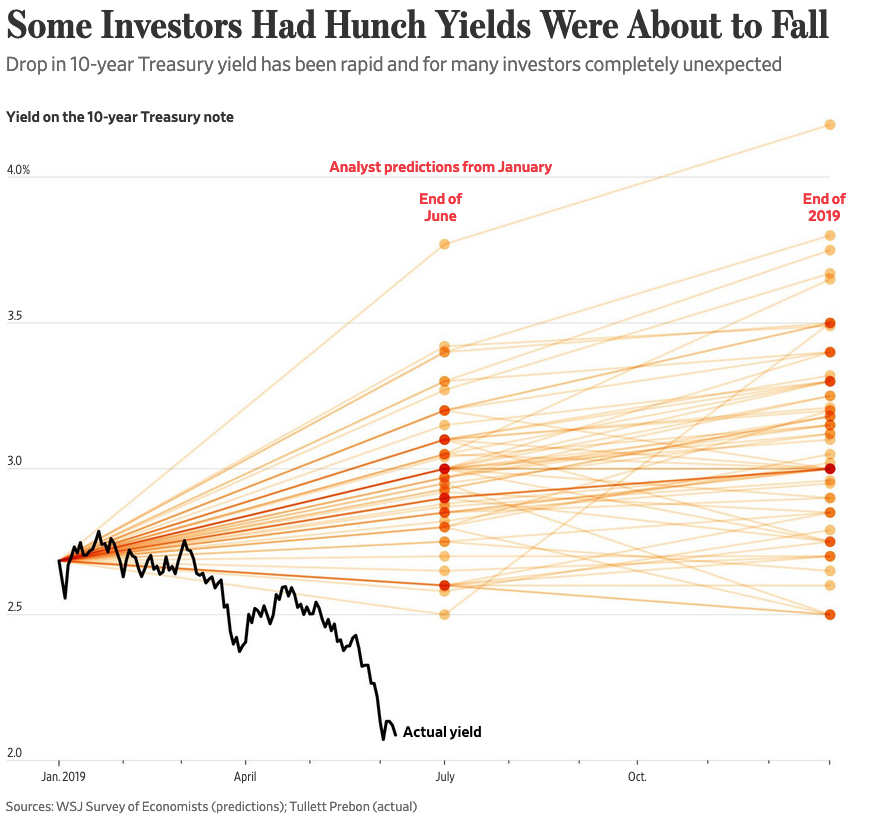
Yield Curve
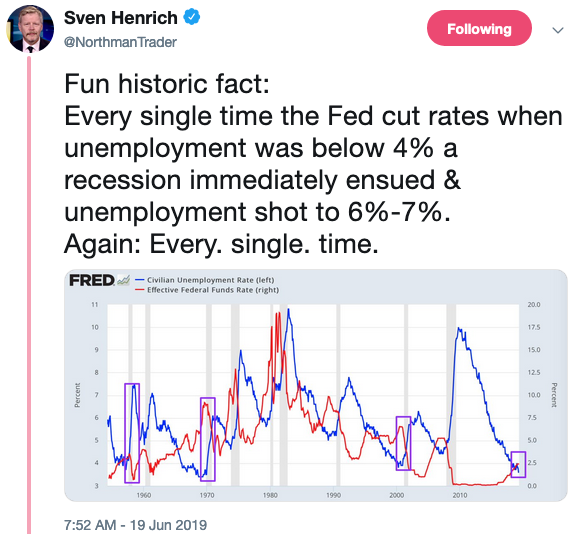
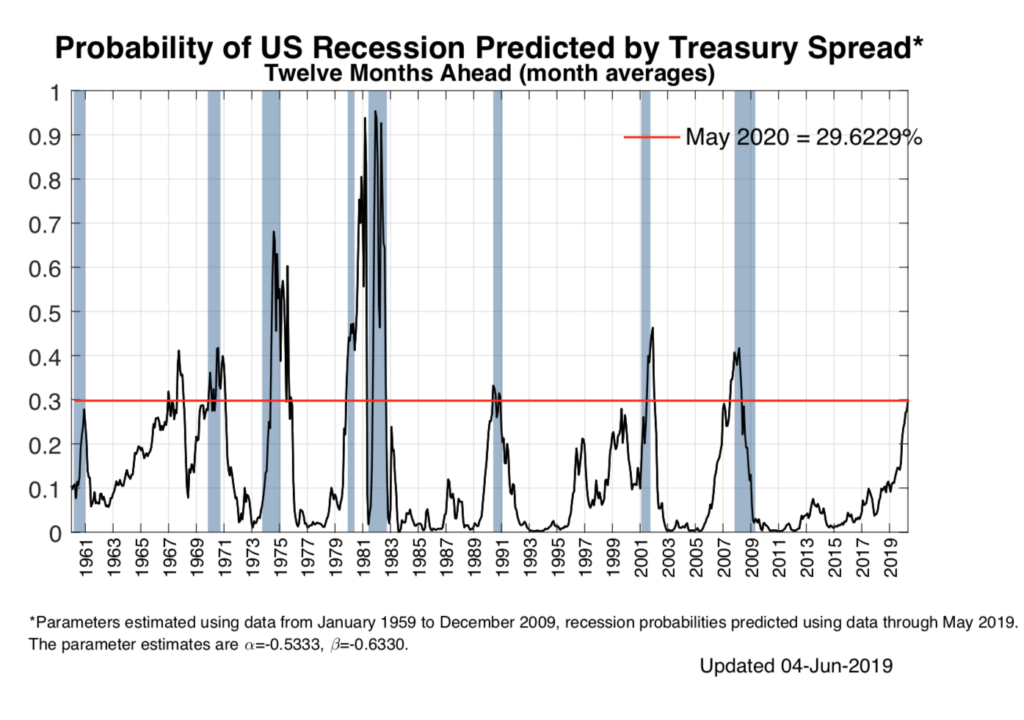
As the adage goes, expansions don’t die of old age, but their footing becomes less sure over time and we are seeing signs of rockier terrain. One sign comes from the yield curve which has been flattening steadily since October 2018 with the spread between the 10-year and the 3-month falling from over 100 basis points to -39. The most widely watched part of the curve, between the 10-year and 2-year, has inverted four times in the past few weeks.
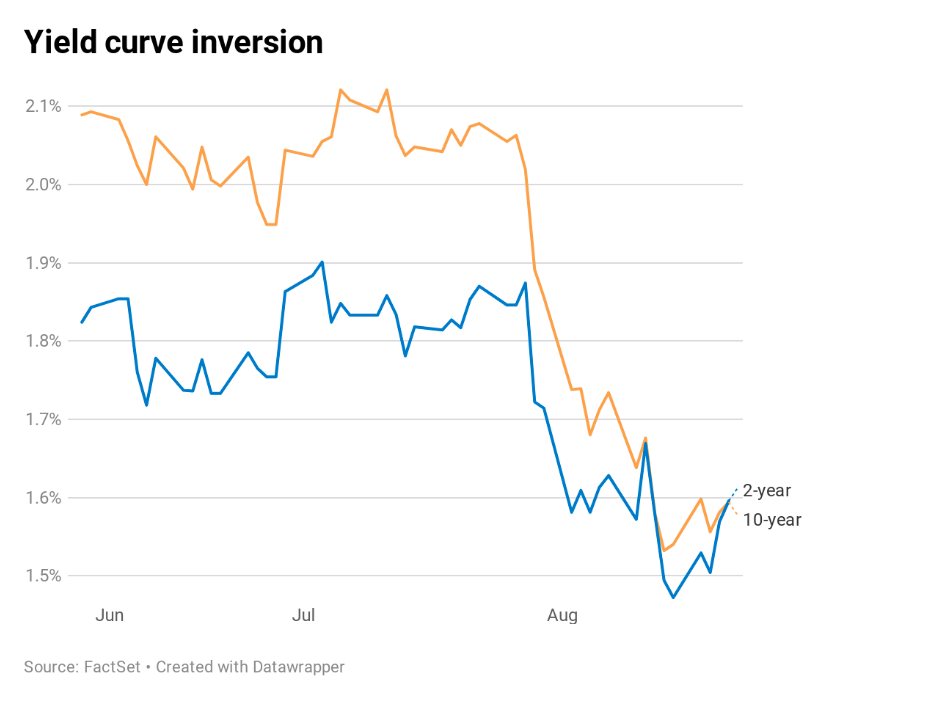
This 2-10 inversion is most closely watched as over the past 50 years it has preceded all seven recessions. Credit Suisse has found that on average a recession hit 22 months after the 2-10 inversion occurred.
The third of August’s four inversions came as Kansas City Federal Reserve President Esther George and Philadelphia Fed President Patrick Harker stated in a CNBC interview that they don’t see the case for additional interest rate cuts following the cut in July. Mr. Market was not looking to hear that.
This past week we also received the meeting minutes from the prior Fed meeting with led to July’s 25 basis point cut which gave the impression of a Fed far less inclined to cut than the market was expecting with most Fed participants seeing July’s cut as part of a recalibration but not part of a pre-set course for future cuts. Keep in mind that central bank rate cuts are a relative game and ECB officials have been signaling a high likelihood of significant accommodative measures at the September meeting, saying the ECB “will announce a package of stimulus measures at its next policy meeting in September that should overshoot investors’ expectations.”
Manufacturing
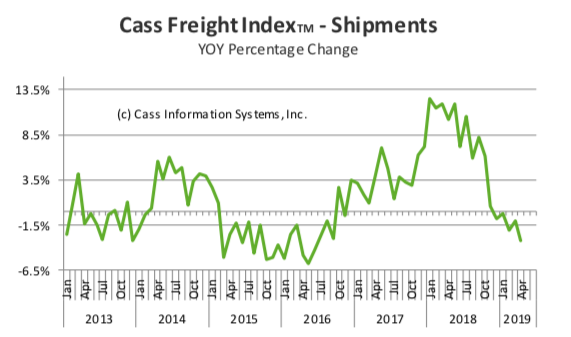
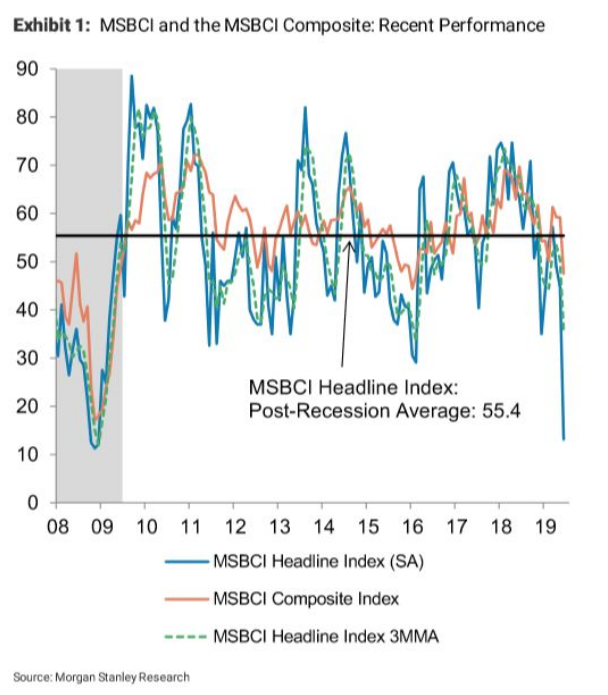
Another source of bumps on the economic road comes from the manufacturing sector, both domestic and international. A recent IHS Markit report found that the US manufacturing sector is in contraction for the first time in nearly a decade as the index fell from 50.4 in July to a 119-month low of 49.9 in August – readings below 50 indicate contraction.
According to the Institute for Supply Management, US manufacturing activity has slowed to a nearly three-year low in July. By August New Orders (a key leading indicator) had dropped by the most in 10 years with export sales falling to the lowest level since August 2009.
New business growth has slowed to its weakest rate in a decade, particularly across the service sector. Survey respondents mentioned headwinds from weak corporate spending based on slower growth expectations both domestically and internationally – likely caused by the ongoing trade war that got much, much worse this past week.
In a note to clients on August 11th, Goldman Sachs stated that fears of the US-China trade war leading to a recession are increasing and that the firm no longer expects a trade deal between the two before the 2020 US election. The firm also lowered its GDP forecast for the US in the fourth quarter by 20 basis points to 1.8%.
Global manufacturing has also been slowing, with just two of the G7 nations, Canada and France, currently showing expansion in the sector. In July, China’s industrial output growth slowed to the weakest level in 17 years.
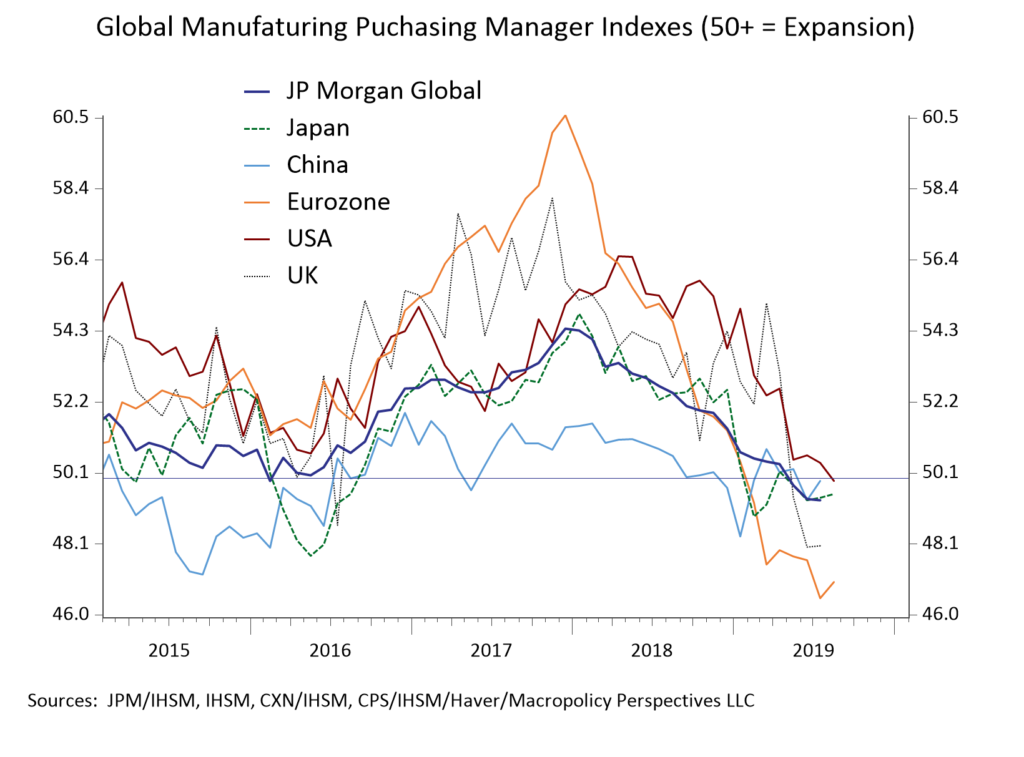
Germany is seeing the most pronounced contraction with its manufacturing PMI dropping from 63.3 in December 2017 to 43.6 this month. German car production has fallen to the levels last seen during the financial crisis.
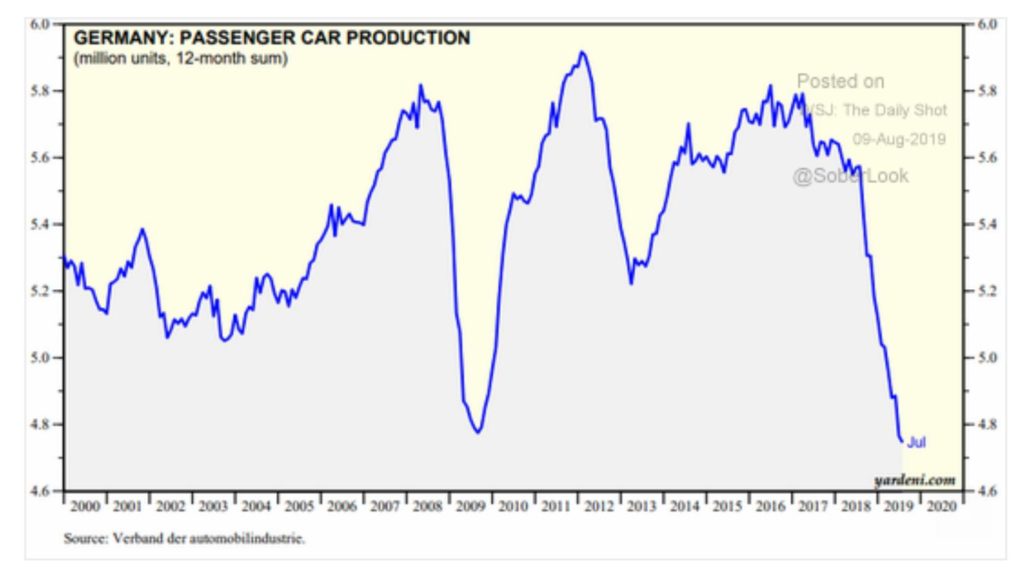
Overall, we see no sign of stabilization in global manufacturing as global trade volumes look to be rolling over, leaving the economy heavily dependent on growth in the Consumer and the Service sectors. Keep in mind that the last time global trade volumes rolled over like this was back in 2008.
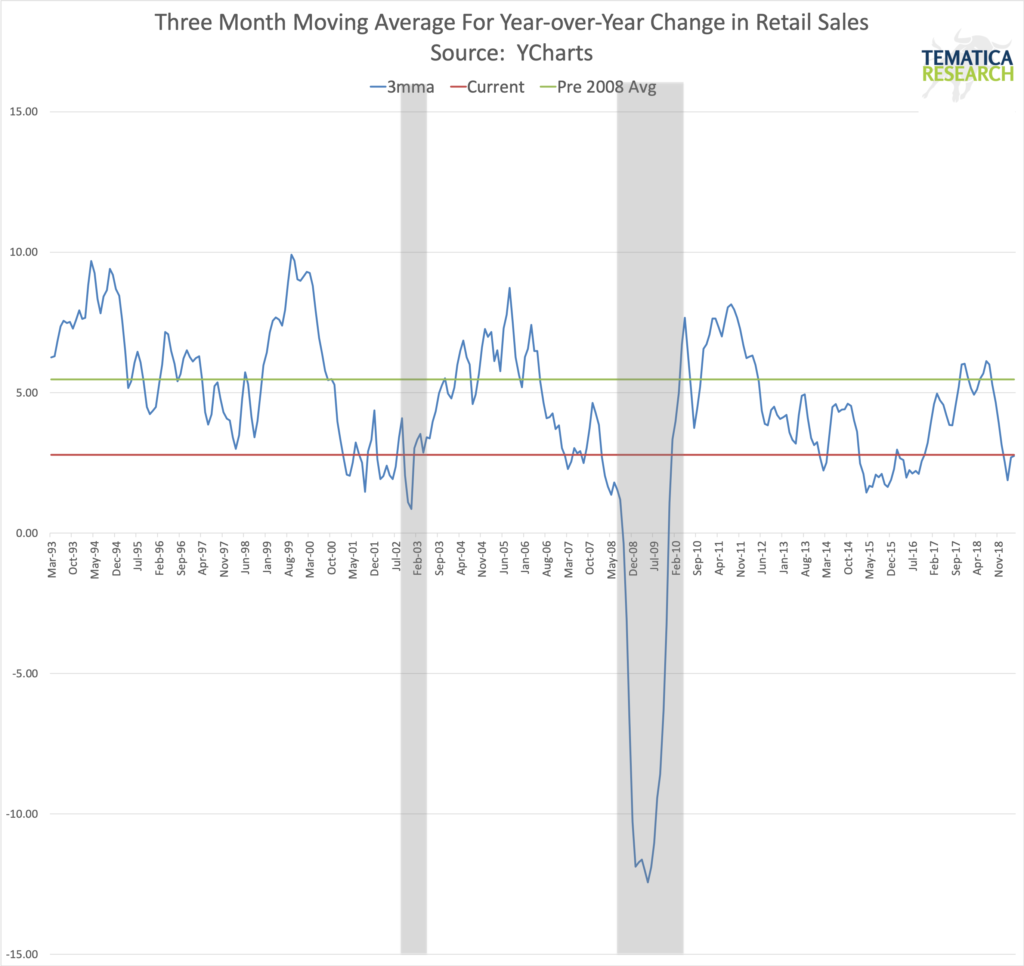
The Consumer
The consumer is yet another source of bumps on the economic road. Ms. Pomboy’s tweet is perfect.
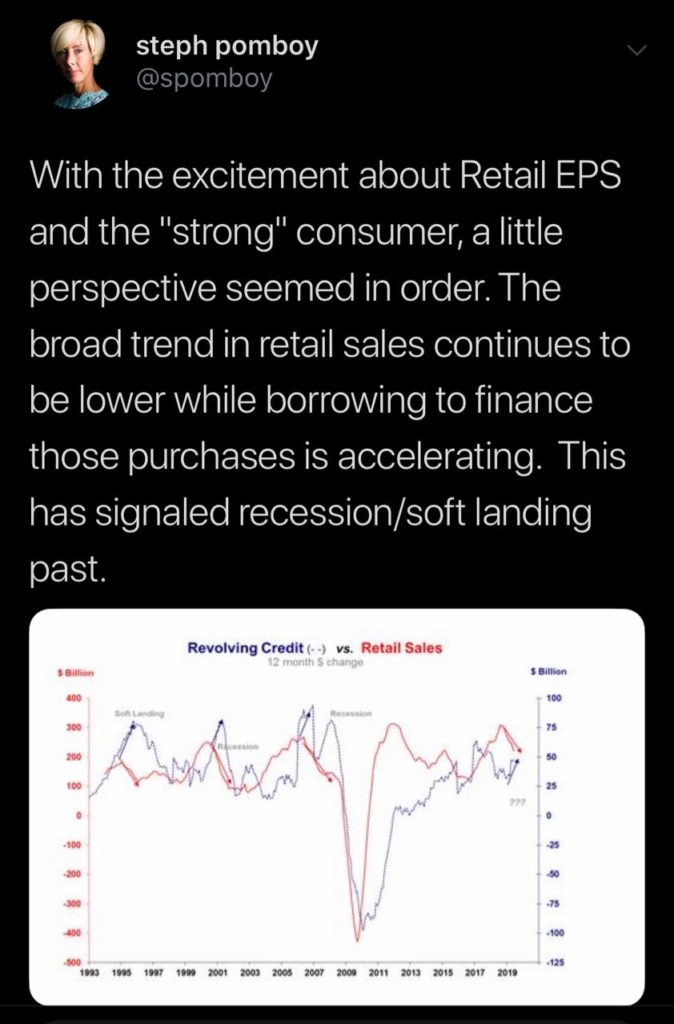
As for that debt, Citigroup recently reported that its credit-card delinquency rate had risen to 2.91% in July from 2.56% in June versus its three-month average of just 1.54%. With all the positive stock moves we’ve seen in retail, keep in mind that the story for many has been more about earnings than actual growth.
For example, Nordstrom (JWN) shares rose 21% after it delivered stronger-than-expected earnings, but that was off of weaker than expected revenue of $3.87 billion versus expectations for $3.93 billion. Nordstrom also slashed net sales guidance for the fiscal year as well as earnings guidance. Management forecast net sales for the year to decrease by about 2%. It previously estimated sales would be flat to 2% down. It also slightly lowered guidance on earnings per share to a range of $3.25 to $3.50, compared with the prior guidance of between $3.25 to $3.65. Did I mention shares rose 21%?
US Consumer sentiment fell to 92.1 in August, the lowest reading for 2019, versus expectations for 97 and down from 98.4 in July. If sentiment continues to degrade, how long will the consumer continue to load up credit cards in order to spend?
Debt
It isn’t just the consumer that is taking on more debt – yet more economic bumps. The federal government deficit rose by $183 billion to $867 billion during just the first 10 months of this fiscal year as spending grew at more than twice the rate of tax collections. The Congressional Budget Office expects the annual budget deficit to be more than 1 TRILLION dollars a year starting in 2022. Total public debt, which includes federal, state and local has reached a record 121% of GDP in 2019, up from 69% in 2000 and 43% in 1980.
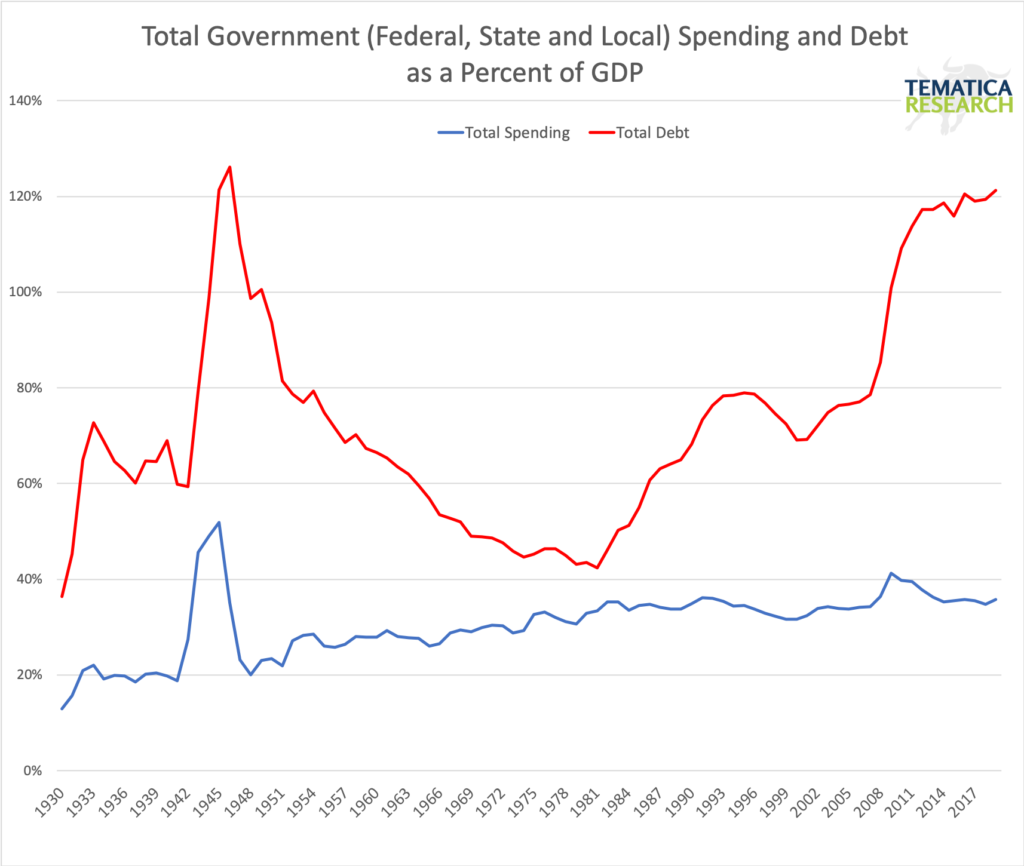
Keep in mind that debt is pulling resources out of the private sector and at such high levels, fiscal stimulus becomes more challenging in times of economic weakness. The only time debt to GDP has been higher was after WWII, but back then we had relatively young population and a rapidly growing labor force compared to today.
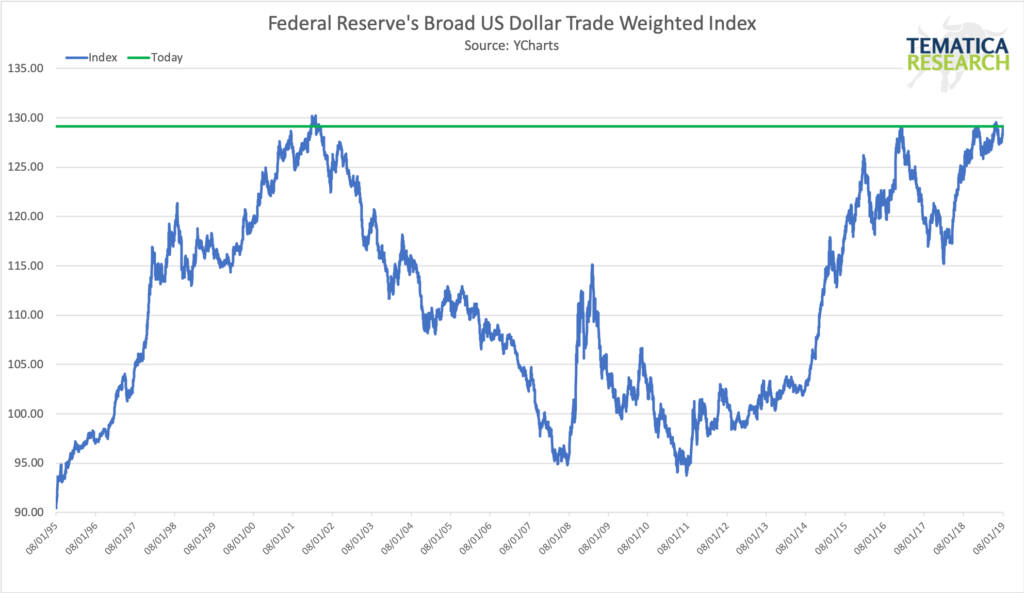
I’ve mentioned before that I am concerned with the strengthening dollar.
I’ve also written many times in the past concerning the dangers that lie in the enormous levels of corporate debt with
Bottom Line
As I said at the start of this piece, this expansion is the longest in post-war history which doesn’t itself mean a recession is imminent, but it does mean that the economy is likely to be more vulnerable. Looking next at the economic indicators we see quite a few that also imply a recession is increasingly likely.
The President’s twitter storm in response to China’s tariffs and the continually rising geopolitical uncertainties that create a strong headwind to any expansions in the private sector only increase risks further. Perhaps by the time you read this piece some part of the rapid escalation of the trade war will have been reversed, as foreign policy has become increasingly volatile day-to-day, but either way, the view from here is getting ugly.